ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Playlist AP® Computer Science: Standard Algorithms 16 videos
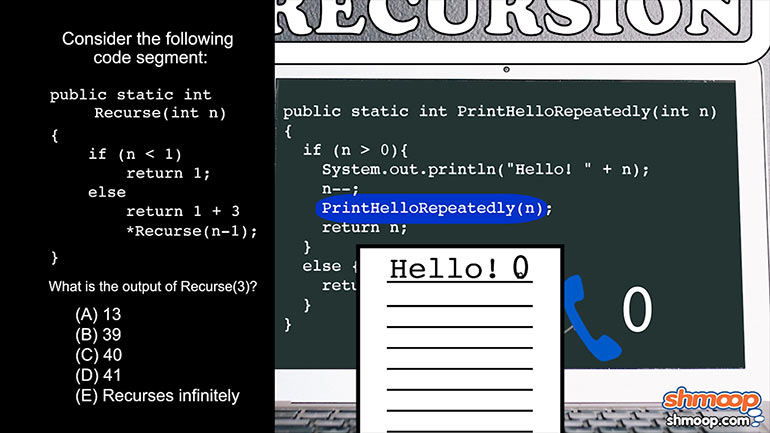
AP Computer Science 1.4 Standard Algorithms. How many times will mystery be called for mystery(n) for n > 1?
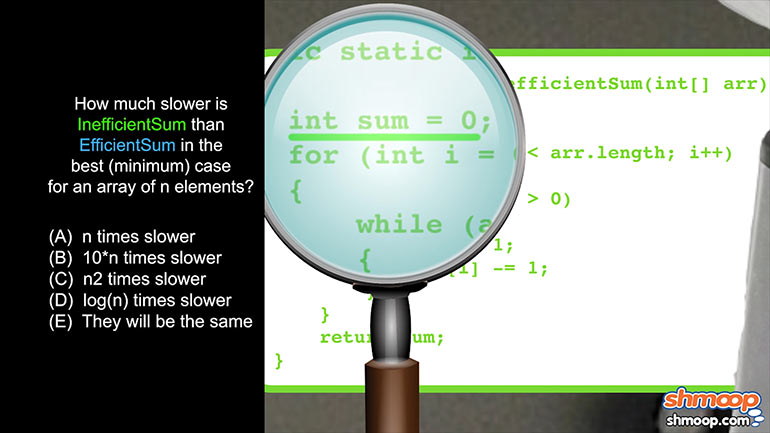
APCS: Standard Algorithms Drill 2, Problem 1. How much slower is InefficientSum than EfficientSum in the best case for an array of n elements?
In this computer science drill question, figure out which implementation will copy one array over to another.
AP Computer Science 4.1 Standard Algorithms 173 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Computer Science 4.1 Standard Algorithms. How much slower is InefficiantSum than EfficientSum in the best case for an array of n elements?
Transcript
- 00:00
Sorry Here's your shmoop news your it's a maze ing
- 00:07
and not at all corny Alright sorry Sometimes we just
- 00:10
do that Alright Moving on you know art ignore it
- 00:12
Don't throw up art How much slower is inefficient Some
- 00:16
than efficient Some in the best minimum case for an
Full Transcript
- 00:19
array of n elements right here in the rays list
- 00:24
go all right here your potential answers How many times
- 00:30
slower like a rap song All right well to answer
- 00:35
this one we'll have to figure out how both methods
- 00:38
work to see exactly what would make one of them
- 00:40
less efficient than the other So for efficient Some were
- 00:44
creating a loop that begins with its iterated at one
- 00:46
and adds the contents of each following array element to
- 00:49
array in deck zero until we reach the end Yeah
- 00:53
in effect index zero becomes the running total as we
- 00:56
travel through the array makes sense and it's pretty efficient
- 00:59
just like the name says inefficient Some creates a separate
- 01:03
variable toe hold are running total then visits each element
- 01:06
of the array as we had done before but here's
- 01:09
the univision part while the value of the current array
- 01:12
element is greater than zero It subtract one from it
- 01:15
and adds one to the some variable Then it checks
- 01:18
it again and again and again And i will keep
- 01:20
doing this until the array element here is zero So
- 01:24
often injure in the array Had a value of say
- 01:26
fifty We'd have to complete this process fifty times If
- 01:29
a were a million six hundred four thousand two hundred
- 01:32
ninety three Well yeah inefficient is the right word for
- 01:35
it The difference is a bit like someone opening a
- 01:37
can of corn and eating each nibble it one by
- 01:39
one versus more standard practise of opening began and chugging
- 01:43
the entire thing right there in a sec That's The
- 01:46
new mcdonald's product It's really cool and pride Okay from
- 01:49
this we can tell that the larger the values aaron
- 01:52
the array the larger the kansas corn would be and
- 01:54
the longer inefficient some would take This question is asking
- 01:57
for the best case scenario And by far the best
- 02:00
case as far as inefficient Some is concerned would be
- 02:02
in a ray full of zeros It could be enormous
- 02:05
Hundreds of thousands of zeros and we'd zip right through
- 02:08
It practically the same speed as efficient some because we'd
- 02:10
be avoiding that tedious wild loop entirely The result in
- 02:14
that best all zero case is that bullet methods would
- 02:17
run at the same speed or at least at such
- 02:20
close speeds that it would be difficult to accurately measure 00:02:22.968 --> [endTime] the difference That'll make her answer
Related Videos
AP Computer Science 3.4 Inheritance, Abstraction, and Polymorphism. Which of the following will satisfy the conditional if statement for boo, str,...
AP Computer Science 1.2 GridWorld Case Study and APIs. What is the direction of the actor?
AP Computer Science 1.4 Standard Algorithms. How many times will mystery be called for mystery(n) for n > 1?
AP Computer Science 2.3 Classes and Objects. Which of the following is correct implementation of the Country class?
AP Computer Science 4.2 Standard Algorithms. What kind of algorithm is the following?