ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
AP Physics 1 Videos 69 videos
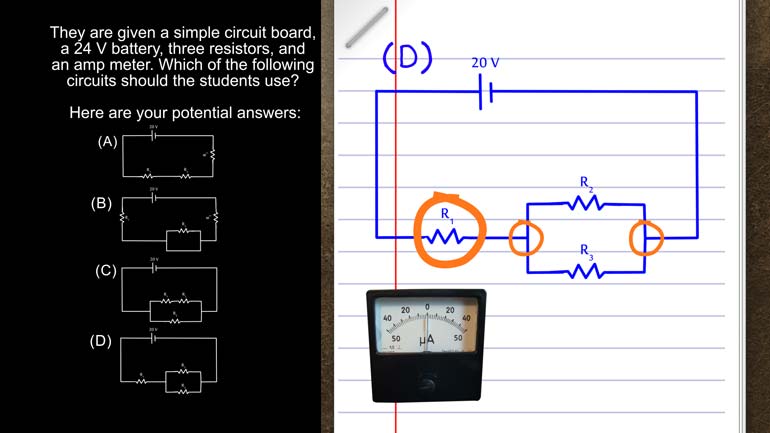
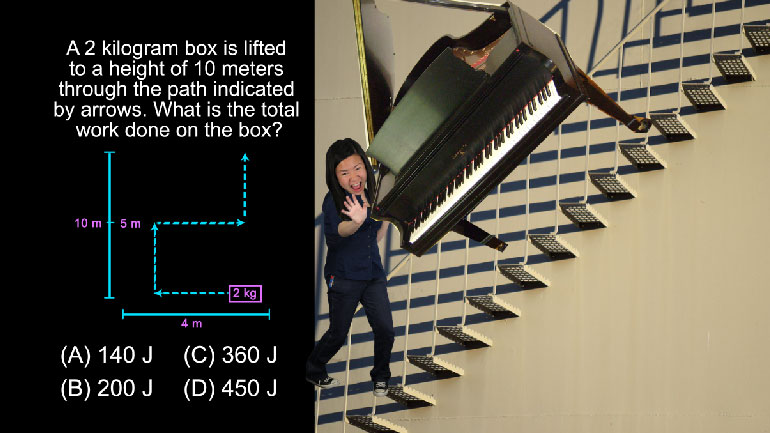
AP Physics 1: 2.4 Changes and Conservation Laws. Which of the following circuits should the students use?
AP Physics 1: 2.5 Changes and Conservation Law. At what point(s) in this situation is energy lost in any form?
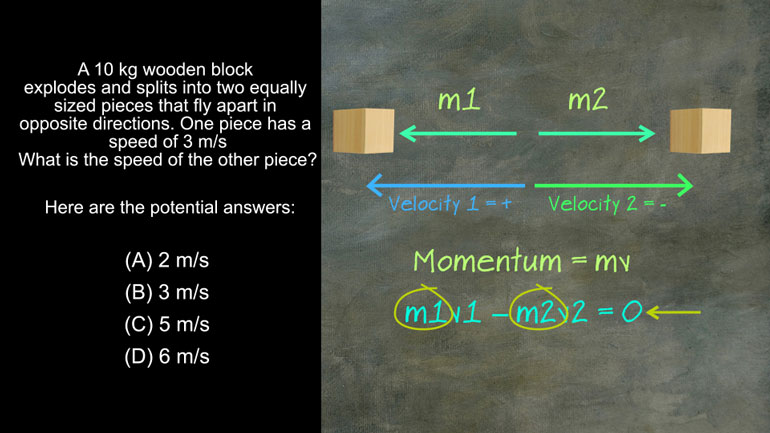
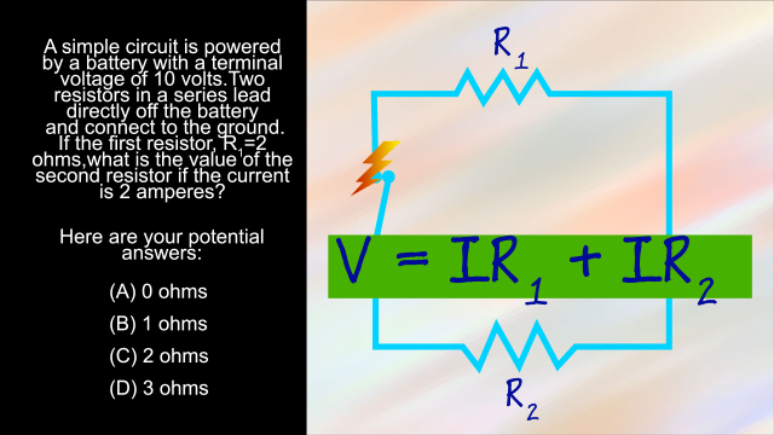
AP Physics 1: 1.4 Changes and Conservation Laws. Find the current across R2.
AP Physics 1: 1.2 Changes and Conservation Laws 214 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Physics 1: 1.2 Changes and Conservation Laws. Why is energy lost in inelastic collisions?
More Video DetailsTranscript
- 00:00
Thank you We sneak And here's your shmoop du jour
- 00:05
brought to you by any elastic collisions which occur when
- 00:09
there's a collision and kinetic energy is lost Elastic collisions
- 00:13
on the other hand are just they're physicist speak for
- 00:15
rubber band fights Those are awesome Okay why is kinetic
Full Transcript
- 00:20
energy lost in in elastic collisions If energy is always
- 00:26
conserved and hear the potential answers logical good questions here
- 00:33
All right so what does happen in an inn elastic
- 00:36
collision Well we know that the law of conservation of
- 00:39
energy can't be broken which is enough to eliminate option
- 00:42
b There are no exceptions the laws of physics that's
- 00:44
why they're called laws people and not suggestions of physics
- 00:48
and option d yeah that's a lawbreaker too Conservation of
- 00:51
energy isn't just on paper it's a real life things
- 00:54
so see eddie but kinetic energy isn't always transferred to
- 00:58
the other object in an inn elastic collision either if
- 01:01
we throw a spitball at a wall and it sticks
- 01:03
there while the wall isn't moving So it hasn't gained
- 01:06
any kinetic energy which rules out eh So we're left
- 01:09
with option c it's the correct answer The kinetic energy
- 01:13
is transformed into a different state Take a look at
- 01:16
captain sticky here jumping from a trampoline onto a wall
- 01:19
He certainly doesn't have any kinetic energy anymore but since
- 01:23
he stuck up there he now has potential energy right
- 01:26
He could fall and kinetic energy can also be transformed
- 01:29
heat energy sound energy and other forms of energy too
- 01:33
Now most real world collisions are at least partially in
- 01:36
elastic after almost things don't perfectly transfer kinetic energy When
- 01:40
they collide there's friction which creates heat energy and objects
- 01:45
can get deformed which takes energy too Think of a
- 01:48
basketball if we bounce a basketball on concrete from a
- 01:51
height of five feet it won't bounce five feet high
- 01:54
it's partly because of gravity and partly because when the
- 01:56
ball hits the ground it compresses slightly then returns to
- 01:59
its normal shape Well that's kinetic energy Taking a different
- 02:02
form is a type of potential energy This is the
- 02:05
same type of potential energy created when we pull a
- 02:08
rubber band back like that And when that rubber band
- 02:10
smack someone in the face or the rear that's called 00:02:14.11 --> [endTime] an act of war it bring it
Related Videos
AP Physics 1: 2.5 Changes and Conservation Law. At what point(s) in this situation is energy lost in any form?
AP Physics 1: 1.4 Waves. Which of the following is technically true for Max as he stands at the edge of oblivion?
AP Physics 1: 1.4 Changes and Conservation Laws. Find the current across R2.
AP Physics 1: 2.4 Changes and Conservation Laws. Which of the following circuits should the students use?
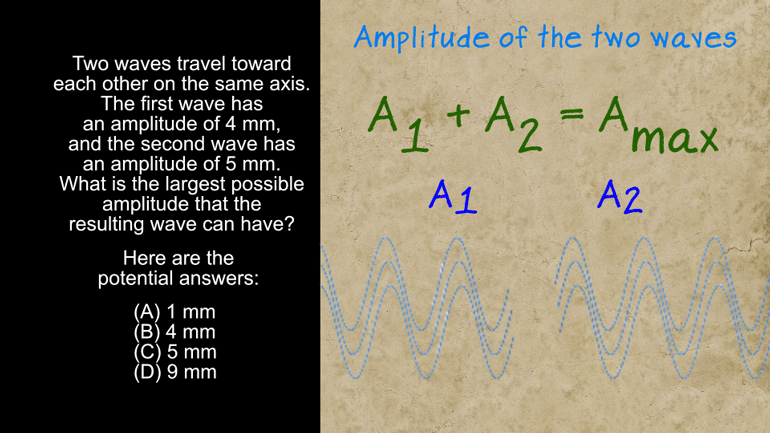
AP Physics 1: 1.5 Waves. What can possibly occur when the two waves reach each other?