ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Learning Videos 9 videos
AP Psychology 2.4 Learning. What is this behavior an example of?
AP Psychology 2.5 Learning. Which concept explains why you might not be able to teach your dog to use the toilet?
AP Psychology 3.3 Learning. An example of a primary reinforcer is what?
AP Psychology 1.3 Learning 11 Views
Share It!
Description:
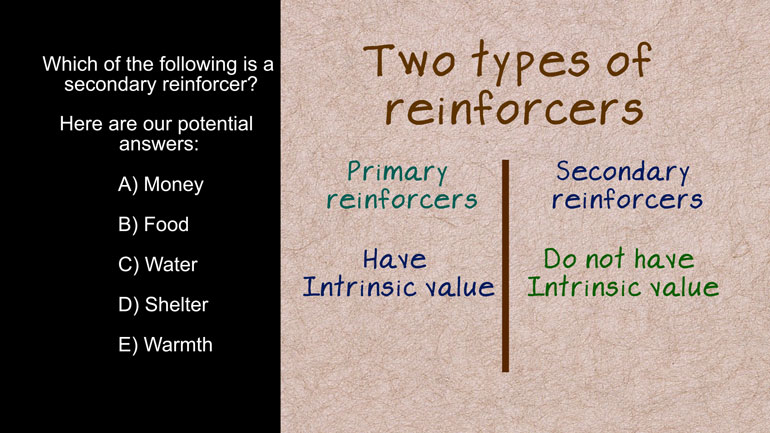
AP Psychology 1.3 Learning. Which of the following is a secondary reinforcer?
Transcript
- 00:04
Here's your schmuck du jour brought to you by money which [Money falling from the air]
- 00:07
definitely does not grow on trees don't be absurd it's 75% cotton so it
- 00:12
obviously grows on plants duh okay here's our question which of the
- 00:17
following is a secondary reinforcer and here are our potential answers....
- 00:21
...okay before we take a look at the answer specifically it's
Full Transcript
- 00:25
probably best we contexualise our terms here exactly what is this reinforcer [Girl reading a book]
- 00:31
business even referring to well if an enforcer is a tough guy hockey player
- 00:35
who fights people is the secondary reinforcer the guy who shows up once the [Hockey player hits another player]
- 00:40
fights over and makes fun of the loser? not quite now what
- 00:45
we're talking about is operant conditioning the modification of
- 00:49
adaptive conscious behaviors based on reinforcement and punishment now there
- 00:53
are two types of reinforcers who reinforce behavior primary and secondary
- 00:58
primary enforcers have intrinsic value while secondary reinforcers do not. To [primary and secondary reinforcer details]
- 01:05
reinforce this idea okay let's take a look at an example all right here's you
- 01:09
this is a super accurate representation of you the viewer sitting at your [Boy sitting at computer desk]
- 01:14
computer now you yes you are studying on shmoop in preparation for your big exam
- 01:20
now there are probably a whole host of reinforcers that encourage you to
- 01:23
consciously and actively study for your exam many of those are primary [Boy studying on computer and parents appear]
- 01:28
reinforcers that have intrinsic value like a hug from your mom when your score
- 01:32
is high on a test or your dad telling you how proud he is of you other primary
- 01:38
reinforcers include being rewarded water when you're thirsty or being able to
- 01:42
rest when you're tired these are all primary motivating factors that have
- 01:46
intrinsic value that is they're valuable for exactly what they are and are
- 01:51
totally real.. secondary reinforcers on the other hand don't have intrinsic
- 01:56
value in other words they're valuable because our society has deemed them
- 02:00
valuable in the case of you and your parents [Boy standing with parents]
- 02:03
secondary reinforcers could be your good grades, acceptance into a good university
- 02:08
or even an academic award they aren't inherently valuable but as a
- 02:13
society we've decided these things have value so now that we understand our
- 02:18
definitions let's take a look at our answers again clearly four of those
- 02:21
answers are primary reinforcers answers B through E all speak to our basic and
- 02:26
biological needs and therefore have intrinsic value money on the other hand [Man with piles of money]
- 02:31
has no intrinsic value we only value money because we as a society have all
- 02:37
agreed to making it a secondary reinforcer in the answer we've been
- 02:42
looking for so we don't know why we all value money so highly just plant the [Girl shaking a piggy bank]
- 02:46
money plant like we did here at shmoop and it froze... we
- 02:51
totally did not do that all right got to go...
Related Videos
AP Psychology 2.2 Social Psychology. Which of the following was an independent variable manipulated in Asch's research?
AP Psychology 1.1 Personality. According to Freud, these three parts of personality are constantly in conflict.
AP Psychology 1.1 Sensation and Perception. The process by which the brain can turn sensory stimuli from the outside world into electrical signals...
AP Psychology 1.1 Social Psychology. Which of the following best describes social psychology?
AP Psychology 1.1 States of Consciousness. Who conducted research on REM sleep deprivations?