ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
ASVAB Videos 95 videos
ASVAB Paragraph Comprehension 1.2 Summary. Which of the following best describes the purpose of this passage?
ASVAB Paragraph Comprehension 2.3 Summary. Which of the following best describes the main idea of this passage?
ASVAB Paragraph Comprehension 1.2 Vocabulary-In-Context. In this passage, the word "illustrious" most nearly means...what?
ASVAB Physical Science 1.3 188 Views
Share It!
Description:
ASVAB: Physical Science Drill 1, Problem 3. An ion is formed when...what?
Transcript
- 00:00
[ musical flourish ]
- 00:02
And here's your Shmoop du jour, brought to you by ions.
- 00:05
They're all charged up.
- 00:07
Like when we chugged that two liter of Mountain Dew.
- 00:09
Yeah. That's what happens to you.
Full Transcript
- 00:11
An ion is formed when... what?
- 00:14
And here are our potential atoms... uh, answers.
- 00:18
[ mumbles ]
- 00:19
Okay, getting right into it. The best answer here is C.
- 00:22
An ion is formed when an atom gains or loses an electron.
- 00:26
That's great, but why is it the answer?
- 00:29
That's why we're here, right?
- 00:30
Otherwise, we'd just be watching funny cat videos
- 00:32
on YouTube. The cat on a roomba? Classic.
- 00:35
An ion is an atom that has a positive or negative electric charge.
- 00:40
And just knowing that gives us enough info to eliminate D.
- 00:43
Two atoms that are chemically joined make a molecule, not an ion.
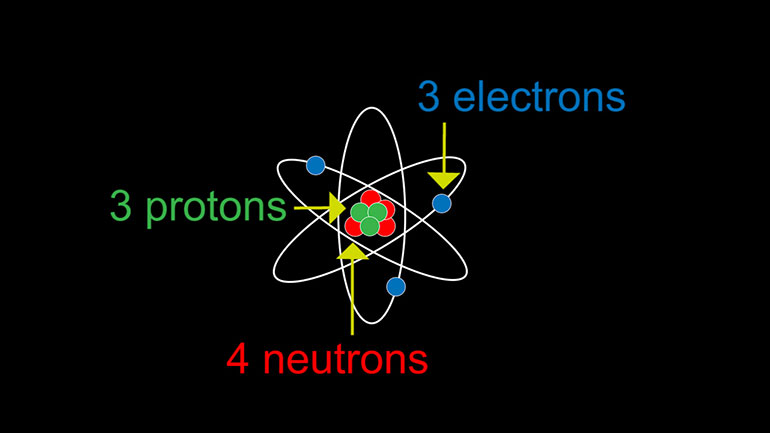
- 00:47
An atom has a nucleus which contains protons
- 00:50
and neutrons. Outside of the nucleus,
- 00:53
electrons are zipping around.
- 00:55
Well, protons are positively charged,
- 00:57
electrons are negatively charged, and neutrons are, well,
- 01:01
neutral. Get the "neut" in there? Yeah.
- 01:03
In a normal, non-ionized atom,
- 01:05
there are as many electrons as there are protons,
- 01:08
so the charges balance themselves out and the atom has no net charge.
- 01:12
Now how would an atom get out of balance?
- 01:14
Well, neutrons aren't gonna make a difference because they don't
- 01:17
have a charge in the first place. So we can get rid of option B.
- 01:20
We can also eliminate A.
- 01:22
The nucleus of an atom is pretty strong,
- 01:24
and in order to change the nucleus of an atom, you need
- 01:26
a huge amount of force. And if you do manage to pull it apart
- 01:29
or push more protons into it, well, you can end up with
- 01:32
a really big bang. Yeah.
- 01:35
But electrons, relatively speaking, are further away from the nucleus
- 01:38
and, out there, sometimes another atom comes along and swipes one of them up.
- 01:42
And, sometimes, an atom picks up a stray electron in the process
- 01:45
and it decides to hang out there for a while, like when
- 01:48
our cousin Ricky came for a weekend and stayed on our couch for six months.
- 01:51
So to bring us back to the beginning, an ion is a charged atom.
- 01:54
We're gonna stick with option C, because gaining or losing an electron
- 01:57
is what gives an atom a positive or negative charge.
- 02:00
We're gonna try to skip the caffeine for a few days.
- 02:02
We've seen our little cousin take a sip of coffee and, trust us,
- 02:04
there's, uh, such thing as being too charged up.
- 02:08
Settle down, settle down...
Related Videos
ASVAB Paragraph Comprehension 1.2 Summary. Which of the following best describes the purpose of this passage?
ASVAB Paragraph Comprehension 1.2 Vocabulary-In-Context. In this passage, the word "illustrious" most nearly means...what?
ASVAB Paragraph Comprehension 1.3 Vocabulary-In-Context. The word "preposterous" most nearly means what?
ASVAB Paragraph Comprehension 2.3 Summary. Which of the following best describes the main idea of this passage?
ASVAB Word Knowledge: Word Roots, Prefixes, and Suffixes Drill 1, Problem 1. Which of these words is closest in meaning to incoherent?